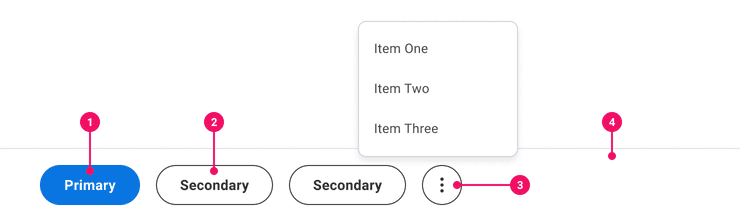
Action Bar
Action Bars contain primary and secondary actions related to a page or task.
Anatomy
- Primary Button: A button that is discoverable and used as the most important action to take on a page.
- Secondary Button: A button or set of buttons that is less important than the Primary Button.
- Overflow Menu: An Icon-Only Secondary Button Variant with an Ellipsis Icon used for responsive screens or small page width to show more actions.
- Container Bar: The Container Bar is used to house action buttons and is anchored at the bottom of the screen.
Usage Guidance
- Primary Buttons should only be used once per screen. If there are other buttons on screen, use the Secondary or Tertiary Buttons. However, Tertiary Buttons should not be on the Action Bar unless it's in the Overflow Menu.
- Action Bars are placed at the bottom of the screen, and will stick as the user scrolls.
- Although actions may change, the placement of the Action Bar should persist until the task is successfully submitted.
- Action Bars can contain up to 3 actions and an Overflow Menu when appropriate.
- If there are more than 3 actions, hide the 4th and other remaining actions in an Overflow Menu that is launched by clicking the Icon Only Secondary Button Variant.
- There should be between 1-7 items to choose from in an Overflow Menu.
- Buttons placed in Action Bars should be grouped logically, either by usage or importance.
When to Use
- Use Action Bars for tasks that require navigating between pages, saving progress, submitting a task, or cancelling a task.
When to Use Something Else
- Consider taking a Button outside of the Action Bar if the action is not related to the progress or status of a task.
- Consider using a Text Button instead of an Action Bar if an action is less popular or less important.
Examples
Basic Example
ActionBar includes a container ActionBar component and the following subcomponent:
ActionBar.List which should contains ActionBar.Item.
In a basic example of an ActionBar there are two buttons. The primary action button should be used
only once and left aligned if content is left to right, followed by secondary buttons. Tertiary
buttons should not be used in the Action Bar.
Icons Example
ActionBar.Item renders a SecondaryButton as default, so it's possible to use other Button props
with ActionBar.Item such as icon or size.
Delete Action Example
ActionBar.Item is a SecondaryButton by default but it's posible to change it to another element,
such as DeleteButton, by using as prop.
Overflow Example
ActionBar container can contain up to 3 actions and an Overflow Menu if there are more than 3
actions, the other remaining actions should be placed into an Overflow Menu that is launched by
clicking the Overflow Button.
Also, ActionBar is a responsive component based on the width of its container. If the rendered
actions exceed the width of the ActionBar.List, an overflow menu will be rendered. This only works
against the dynamic API where you give the ActionBarModel an array of items to be rendered. The
dynamic API handles the React key for you based on the item's identifier. The dynamic API requires
either an id on each item object or a getId function that returns an identifier based on the
item. The below example uses an id property on each item.
The dynamic API takes in any object, but since nothing is known about your object, a render prop is necessary to instruct a list how it should render.
Change Action Bar container size
The number of visible buttons can also be adjusted by using the model's maximumVisible attribute.
You can change it from the default of 3 to any number greater than 1 and less than items.length.
Component API
ActionBar
ActionBar is a container component that is responsible for creating an and sharing it with its subcomponents using React context. It does not represent a real element.
<ActionBar items={[]}>{Child components}</ActionBar>
Alternatively, you may pass in a model using the hoisted model pattern.
const model = useActionBarModel({items: [],});<ActionBar model={model}>{Child components}</ActionBar>;
Props
Props extend from . If a model is passed, props from ActionBarModelConfig are ignored.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
children | ReactNode | The contents of the ActionBar. Can be | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
ActionBar.List
ActionBar.List is a element. It is a container for
subcomponents. To render an overflow button for
ActionBar with overflow behavior overflowButton prop with overflow button component as a
value should be passed.
// without overflow<ActionBar.List>{ActionBar.Items}</ActionBar.List>// with overflow<ActionBar.List overflowButton={<ActionBar.OverflowButton aria-label="More actions"/>}>{ActionBar.Items}</ActionBar.List>
Layout Component
ActionBar.List supports all props from thelayout component.
Props
Props extend from div. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
children | (( | If items are passed to a | |
overflowButton | ReactNode |
| |
cs | | The
| |
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | div |
ref | React.Ref<R = div> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
useOverflowListMeasure
This elemProps hook measures a list and reports it to an OverflowListModel. This is used in
overflow detection.
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {
ref: (instance: | null) => void;
}ActionBar.Item
ActionBar.Item is a button element, by default it's a SecondaryButton unless an as
prop is passed.
<ActionBar.Item as={PrimaryButton} onClick={() => console.log('first action')}>First Action</ActionBar.Item>
Props
Props extend from . Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
children | ReactNode | The contents of the action item. This will be the accessible name of the action for screen readers.
| |
data-id | string | The identifier of the action. This identifier will be used for correct overflow behavior. If this property is not provided, it will default to a string representation of the the zero-based index of the Item when it was initialized. | |
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | |
ref | React.Ref<R = > | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
ActionBar.OverflowButton
Layout Component
ActionBar.OverflowButton supports all props from thelayout component.
Props
Props extend from button. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
aria-label | string | ||
variant | 'inverse' | Variant has an option for | |
iconPosition | 'start' | 'end' | Button icon positions can either be | 'start' |
fill | | The fill color of the SystemIcon. This overrides | |
color | | The color of the SystemIcon. This defines | |
size | | There are four button sizes: | |
styles | | ||
shouldMirror | boolean | If set to | false |
background | | The background color of the SystemIcon. | |
cs | | The
| |
children | ReactNode | ||
icon | | The icon of the Button.
Note: not displayed at | |
accent | | The accent color of the SystemIcon. This overrides | |
accentHover | | The accent color of the SystemIcon on hover. This overrides | |
backgroundHover | | The background color of the SystemIcon on hover. | |
colorHover | | The hover color of the SystemIcon. This defines | |
fillHover | | The fill color of the SystemIcon on hover. This overrides | |
colors | | Override default colors of a button. The default will depend on the button type | |
fillIcon | boolean | Whether the icon should received filled (colored background layer) or regular styles.
Corresponds to | |
shouldMirrorIcon | boolean | If set to | false |
grow | boolean | True if the component should grow to its container's width. False otherwise. | |
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | button |
ref | React.Ref<R = button> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
useActionBarOverflowButton
(
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {
aria-haspopup: boolean;
},
,
(
(model: ) => ,
)
)ActionBar.Menu
Basic type information:
MenuModel
Accessibility Guidelines
Keyboard Interaction
Each Button in the Action Bar must have a focus indicator that is highly visible against the background and against the non-focused state. Refer to Accessible Colors for more information.
Action Bar must support the following keyboard interactions:
Tab: focus each Button element in the Action BarEnterorSpace: activate focused Button elementEsc: dismiss overflow menu of the action bar (if applicable)- [With overflow]
Up ArroworDown Arrow: navigates among the overflow menu items
Screen Reader Interaction
Action Bar must communicate the following to users:
- The accessible name for each button in the action bar
- The “more actions” icon button has an attached menu or “popup” (if applicable)
- Total number of menu items in the overflow menu (if applicable)
Design Annotations Needed
No design annotations are needed for Action Bar
Implementation Markup Needed
- An
aria-labelstring is required for the overflow icon-only Button variants and accessible tooltips can show the icon's name for everyone. - Action Bar can be rendered as a
<section>element with anaria-labelstring to enable a landmark region for screen reader users. - [Included in component] The overflow icon-only Button variants require an
aria-haspopup=”true”andaria-expandedattribute for the attached menu. - [Included in component] The menu container must have an ARIA
role=“menu”attribute. - [Included in component] All child elements inside the menu container must have an ARIA
role=“menuitem”attribute.
Content Guidelines
- When naming buttons within an Action Bar, refer to the Buttons and Calls to Action section of the Content Style Guide.
Can't Find What You Need?
Check out our FAQ section which may help you find the information you're looking for.
FAQ Section