Tabs
Allows the user to alternate between related views while remaining in the same context.
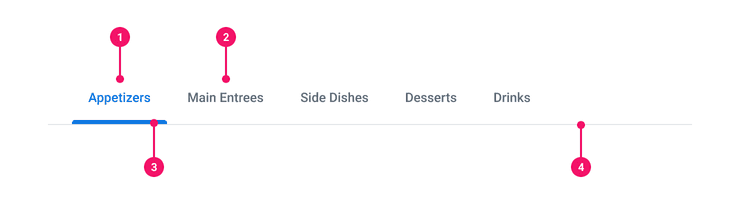
Anatomy
- Active Tab: The tab that is selected and currently displaying it's contents.
- Inactive Tab: All of the other unselected, available tabs.
- Active Chip: Highlights the active tab.
- Divider Line: Spans the width of the entire tabs container separating the tab set from its contents.
Usage Guidance
- Tabs are used to help the user navigate through information while remaining in context of the page. This is the most important reason to use Tabs. Users should not navigate to a different page when interacting with Tabs.
- Content that is grouped within a Tab should always be related so that the user knows what to expect when they navigate each Tab. Never force users to switch back and forth between Tabs to complete a task.
- Tab labels should be concise, scannable, and descriptive of their contents. Avoid using multiple words for Tab labels. Never use icons. To reduce cognitive load and a cluttered UI, avoid using more than 6 Tabs.
- Tabs should directly relate to the page section they’re within.
- The Tab divider line should span the full width of its container and create a clear distinction between what’s under the Tab sections and the rest of the page.
- Do not use Tabs as a primary form of navigation.
- When there are too many tabs to display at once, use the overflow menu to indicate that more Tabs are available.
- The recommended minimum width of a tab is 88px, standard padding to the left and right is 24px, and minimum padding is 16px.
- You can place most components within Tabs, because they operate like mini-pages. For example, Grids, Field Sets, and Prompts can all be added within a tabbed page.
- You can use fixed Tabs, especially when the contents of a tab is scrollable.
When To Use
- When content can be grouped into logical sections in order to avoid overwhelming the user with a lot of information. Tabs should cater for distinct groups of information.
- To alternate between two or more sections of organized content while keeping the user in-context of the greater UI.
- Use Tabs to help section off and organize related content.
- When you have an abundance of related content to house in a small container.
When To Use Something Else
- Consider an alternative solution if the information within multiple Tabs needs to be viewed simultaneously. Tabs are not suitable for comparing information or data, as it forces the user to rely on short term memory when switching back and forth between Tabs.
- Consider using a more prominent, alternative form of navigation when there is a need for more than 6 or 7 Tabs.
- Avoid using Tabs within a card UI.
- If the content on a page is cohesive and doesn’t take up too much space, Tabs are likely unnecessary.
- When Tabs are already being used on the page.
Variations
| Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Default/Standard | Should be used in most use cases for tabs. |
| Full-Width | Exclusively used in smaller containers ~300-400px width (e.g. within side panels or responsive UI).
|
| Wrapped Tabs | Edge case for when there is a requirement to have lengthy or multiple words for a Tab label.
|
Touch Based Behavior
Touch Based behavior for Tab compnents on web adapt and mimic the mobile experience to allow overflow when the tab text stretches past the width of the users’ screen. These Tabs support mobile behavior based on modality and help support WebView users. Touch Based behavior for Tabs will switch from displaying an overflow menu to become scrollable from left to right in order to replicate a mobile experience when viewing a WebView screen (not a native mobile screen) on a mobile device.
States and Behavior
- By default, Tabs should always contain one Tab with an active state.
- Only one Tab can have an active state at a time.
- The inactive state of a Tab can inherit a hover, focus, and selected state.
- The active state of a Tab can only inherit a focus state.
Examples
Basic Example
Tabs includes a container Tabs component and the following subcomponents which can be composed
in a variety of ways: Tabs.List, Tabs.Item and Tabs.Panel. It follows the
W3 Tabs specification.
In this example, we set up a basic Tabs component with five tabs. This example uses a static API
that does not support overflow.
Overflow Tabs
Tabs is a responsive component based on the width of its container. If the rendered tabs exceed the
width of the Tabs.List, an overflow menu will be rendered. This only works against the dynamic API
where you give the TabsModel an array of items to be rendered. The dynamic API handles the React
key for you based on the item's identifier. The dynamic API requires either an id on each item
object or a getId function that returns an identifier based on the item. The below example uses an
id property on each item.
The dynamic API takes in any object, but since nothing is known about your object, a render prop is necessary to instruct a list how it should render.
Change Tabs container size
Hoisted Model
By default, Tabs will create and use its own model internally. Alternatively, you may
configure your own model with useTabsModel and pass it to Tabs via the model prop. This
pattern is referred to as
hoisting the model
and provides direct access to its state and events outside of the Tabs component.
In this example, we set up external observation of the model state and create an external button to trigger an event to change the active tab.
Named Tabs
Tabs.Item and Tabs.Panel both take an optional data-id attribute that is used for the
onActivate callback. This example is identical to the Basic Example, but with tabs named using
data-id for the Tabs.Item and Tabs.Panel subcomponents.
Right-to-Left (RTL)
Tabs supports right-to-left languages when specified in the CanvasProvider theme.
Disabled Tab
Set the disabled prop of a Tabs.Item to true to disable it.
Tab Icons
Tabs can have icons. Use the Icon and Text subcomponents.
Alternative Tab Stop
By default, tab panels are focusable for accessibility. If the contents of a tab panel have a
focusable element, you may disable this default behavior by setting the tabIndex prop of
Tabs.Panel to undefined. This example has a tab panel with a focusable button.
Contents of First Tab. The tab panel is no longer focusable, but the button is. It may be desirable to disable focus on the tab panel and allow focus to flow into the tab panel to the first focusable element.
Single Tab Panel
The compound component pattern allows for advanced composition. For example, Tabs can be composed
to have only a single Tabs.Panel using attribute overrides and callbacks. More information about
attributes and callbacks can be found in the prop tables below for each subcomponent.
In this example, we use a hoisted model and the activeTab property of the state to show content
from the contents object.
Dynamic Tabs
The Tabs.Item component takes in an optional index property if you want to specify the position
of a tab. If not defined, by default it will append tabs to the end. In this example, our tabs are
stored as an array in the state, and we have a fixed tab at the end that can add new tabs to that
array.
Component API
Tabs
Tabs is a container component that is responsible for creating a and sharing
it with its subcomponents using React context. It does not represent a real element.
<Tabs onSelect={data => console.log('Selected tab', data.id)}>{child components}</Tabs>
Alternatively, you may pass in a model using the hoisted model pattern.
const model = useTabsModel({onSelect(data) {console.log('Activated Tab', data.id);},});<Tabs model={model}>{child components}</Tabs>
See Configuring a Model for more information on model configuration.
Props
Props extend from . If a model is passed, props from TabsModelConfig are ignored.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
children | ReactNode | The contents of the Tabs. Can be | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
Tabs.List
Tabs.List is a <div role="tablist"> element. It is a container for subcomponents.
<Tabs.List>{Tabs.Items}</Tabs.List>
Layout Component
Tabs.List supports all props from thelayout component.
Props
Props extend from div. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
children | ((item: T) => ReactNode) | ReactNode | If items are passed to a | |
overflowButton | ReactNode | ||
cs | | The
| |
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | div |
ref | React.Ref<R = div> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
useTabsList
(
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {
role: 'tablist';
overflowX: 'auto' | undefined;
},
,
)Tabs.Item
Tabs.Item is a <button role="tab"> element. Each Tabs.Item is associated with a
Tabs.Panel either by a data-id attribute or by the position in the list. If a data-id
is provided, it must match the data-id passed to the corresponding Tabs.Panel component.
<Tabs.Item data-id="first">First Tab</Tabs.Item>
Layout Component
Tabs.Item supports all props from thelayout component.
Props
Props extend from button. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
index | number | Optionally pass index to tab item. This should be done if | |
children | ReactNode | The contents of the tab item. This will be the accessible name of the tab for screen readers.
Often, this is text. Icons are also supported. Using
| |
data-id | string | The identifier of the tab. This identifier will be used in change events and for | |
id | string | Optional id. If not set, it will inherit the ID passed to the | |
aria-controls | string | Part of the ARIA specification for tabs. This attributes links a | |
aria-selected | boolean | Part of the ARIA specification for tabs. Lets screen readers know which tab is active. This
should either be | |
tabIndex | number | Part of the ARIA specification for tabs. The currently active tab should not have a | |
cs | | The
| |
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | button |
ref | React.Ref<R = button> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
useTabsItem
(
(
model: ,
elemProps: {
data-id: string;
},
ref: React.Ref
) => {
type: 'button';
role: 'tab';
aria-selected: boolean;
aria-controls: string;
},
,
,
,
)Tabs.Item.Icon
Layout Component
SystemIcon supports all props from thelayout component.
Props
Props extend from span. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
icon | | The icon to display from | |
size | number | string | The size of the SystemIcon in | |
accent | string | The accent color of the SystemIcon. This overrides | |
accentHover | string | The accent color of the SystemIcon on hover. This overrides | |
background | string | The background color of the SystemIcon. | |
backgroundHover | string | The background color of the SystemIcon on hover. | |
color | string | The color of the SystemIcon. This defines | |
colorHover | string | The hover color of the SystemIcon. This defines | |
fill | string | The fill color of the SystemIcon. This overrides | |
fillHover | string | The fill color of the SystemIcon on hover. This overrides | |
shouldMirror | boolean | If set to | false |
cs | | The
| |
children | ReactNode | ||
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | span |
ref | React.Ref<R = span> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If |
Tabs.Item.Text
Props
Props extend from span. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
children | React.ReactNode | ||
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | span |
ref | React.Ref<R = span> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If |
Tabs.Panel
Tabs.Panel is a <div role="tabpanel"> element. It is focusable by default. Each
Tabs.Panel is controlled by a Tabs.Item either by a data-id attribute or by the
position in the list. If a data-id is provided, it must match the data-id passed to the
corresponding Tabs.Item component.
<Tabs.Panel data-id="first">{contents of tab panel}</Tabs.Panel>
Layout Component
Tabs.Panel supports all props from thelayout component.
Props
Props extend from div. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
children | ReactNode | The contents of the TabPanel. | |
data-id | string | The identifier of the tab. This identifier will be used in change events and for | |
tabIndex | number | Part of the ARIA specification for tabs. By default, all | |
cs | | The
| |
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | div |
ref | React.Ref<R = div> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
useTabsPanel
(
model: ,
elemProps: {
data-id: string;
item: <any>;
},
ref: React.Ref
) => {
role: 'tabpanel';
aria-labelledby: string;
hidden: boolean;
id: string;
tabIndex: 0;
}Tabs.Panels
Optional subcomponent of tabs that makes dealing with dynamic tabs easier. Tabs.Panels only
works if the model is given an array of items.
const items = [{ id: '1', name: 'first' }]<Tabs items={items}>{tab list}<Tabs.Panels>{item => <Tabs.Panel>Contents of {item.name}</Tabs.Panel>}</Tabs.Panels></Tabs>
Props
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
children | ((item: T) => ReactNode) | ReactNode | ||
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
Tabs.OverflowButton
The overflow button of a Tabs.List. When a tab list overflows, this overflow button is
rendered. Overflow only works when the model is given an array of items.
<Tabs items={items}><Tabs.List overflowButton={<Tabs.OverflowButton>More</Tabs.OverflowButton>}>{dynamic tab items}</Tabs.List></Tabs>
Props
Props extend from button. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
children | ReactNode | The label text of the Tab. | |
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | button |
ref | React.Ref<R = button> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
useTabsOverflowButton
(
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {
aria-haspopup: true;
},
,
(
(model: ) => ,
)
)Tabs.MenuPopper
Props
Props extend from div. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
anchorElement | <Element> | Element | null | The reference element used to position the Popper. Popper content will try to follow the
| |
children | ((props: { | The content of the Popper. If a function is provided, it will be treated as a Render Prop and
pass the | |
getAnchorClientRect | () => | When provided, this optional callback will be used to determine positioning for the Popper element
instead of calling | |
open | boolean | Determines if | true |
placement | | The placement of the | |
fallbackPlacements | [] | Define fallback placements by providing a list of | |
onPlacementChange | (placement: ) => void | A callback function that will be called whenever PopperJS chooses a placement that is different
from the provided | |
popperOptions | <PopperOptions> | The additional options passed to the Popper's | |
portal | boolean | If false, render the Popper within the
DOM hierarchy of its parent. A non-portal Popper will constrained by the parent container
overflows. If you set this to | true |
popperInstanceRef | Ref<> | Reference to the PopperJS instance. Useful for making direct method calls on the popper
instance like | |
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | div |
ref | React.Ref<R = div> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
usePopupPopper
Adds the necessary props to a component. Used by the
subcomponent.
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {
open: boolean;
anchorElement: <>;
ref: (instance: | null) => void;
onPlacementChange: (placement: ) => void;
}Tabs.Menu
The overflow menu of the Tabs component. If there isn't enough room to render all the tab items, the extra tabs that don't fit will be overflowed into this menu.
<Tabs.Menu.Popper><Tabs.Menu.Card><Tabs.Menu.List>{(item: MyTabItem) => <Tabs.Menu.Item data-id={item.id}>{item.text}</Tabs.Menu.Item>}</Tabs.Menu.List></Tabs.Menu.Card></Tabs.Menu.Popper>
This component references the component.
Model
useTabsModel
The TabsModel extends the Collection
System. Tabs have tab items and
panels. Tabs can be overflowed if there isn't enough room to render and will overflow to a
sub-model.
const model = useTabsModel({onSelect(data) {console.log('Selected Tab', data)}})<Tabs model={model}>{Tabs child components}</Tabs>
useTabsModel (config: ): Specifications
| Given | When | Then |
|---|---|---|
| the Basic story is rendered |
| |
| the Basic story is rendered |
| |
| the Basic story is rendered |
| |
| the Basic story is rendered |
| |
| the Basic story is rendered |
| |
| the Basic story is rendered |
| |
| the Basic story is rendered |
| |
| the Basic story is rendered |
| |
| the Basic story is rendered |
| |
| the Basic story is rendered |
| |
| the Basic story is rendered |
| |
| the Basic story is rendered |
| |
| the Basic story is rendered |
| |
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
| |
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
| |
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
| |
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
| |
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
| |
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
| |
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
| |
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
| |
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
| |
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
| |
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
| |
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
| |
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
| |
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the Named Tabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the DisabledTab story is rendered |
|
|
| the DisabledTab story is rendered |
|
|
| the DisabledTab story is rendered |
|
|
| the DisabledTab story is rendered |
|
|
| the DisabledTab story is rendered |
|
|
| the DynamicTabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the DynamicTabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the DynamicTabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the DynamicTabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the DynamicTabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the DynamicTabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the DynamicTabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the DynamicTabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the DynamicTabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the DynamicTabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the DynamicTabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the DynamicTabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the DynamicTabs story is rendered |
|
|
| the LeftToRight story is rendered |
|
|
| the LeftToRight story is rendered |
|
|
| the LeftToRight story is rendered |
|
|
| the LeftToRight story is rendered |
|
|
| the LeftToRight story is rendered |
|
|
| the LeftToRight story is rendered |
|
|
| the LeftToRight story is rendered |
|
|
| the LeftToRight story is rendered |
|
|
| the LeftToRight story is rendered |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
| Could not find a "given". Check the spec file. |
|
|
Accessibility Guidelines
Keyboard Interaction
Each tab must have a focus indicator that is highly visible against the background and against the non-focused state. Refer to Accessible Colors for more information.
Tabs must support the following keyboard interactions:
Tab: focus the active tab elementLeft ArroworRight Arrow: move focus to the previous or next tab elementEnterandSpace: activate the focused tab element- Alternative Tab Stop :
tabpanelcan optionally be included in focus order to improve discoverability for screen readers, and allow scrolling with the keyboard when the height is fixed.
Screen Reader Interaction
Tabs must communicate the following to users:
- The focus is placed on a tab control
- Which page tab in the set is currently selected
- How many total number of tabs are available
Design Annotations Needed
No design annotations needed.
Implementation Markup Needed
- Interactive elements are not allowed inside of a
tablistortabelement. - [Included in component] All tab buttons must have a
role="tab", inside of a parent element withrole="tablist"attribute. - [Included in component] All tabs are required to have an
aria-selected="false"attribute, except for the actively selected tab, must be set to“true”. - [Included in component] The content area container for the
tablist, must have arole="tabpanel"attribute and anaria-labelledbyattribute referencing the uniqueidof the active tab element.
Resources
Content Guidelines
- When writing tab labels, be concise and avoid using multiple words when possible. Labels should clearly describe the contents of the tab to the user.
- The page or page section title (if applicable) should make clear sense when placed after the tab name. Try to imagine the page title is a noun after the tab label. For example: If the page is titled “Fruit”, and the tabs are labeled “ripe” and “rotten”. You could read it in your head as “ripe fruit” or “rotten fruit”.
- Refer to the UI Text > Tabs section of the Content Style Guide when writing tab labels.
Can't Find What You Need?
Check out our FAQ section which may help you find the information you're looking for.
FAQ Section