Skeleton
A Skeleton is a low-fidelity visual placeholder that represents the loading of interface elements before they have displayed on the page. Appearing as a blank version of the page, it mitigates focus on the loading process and improves the user’s perceived load time.
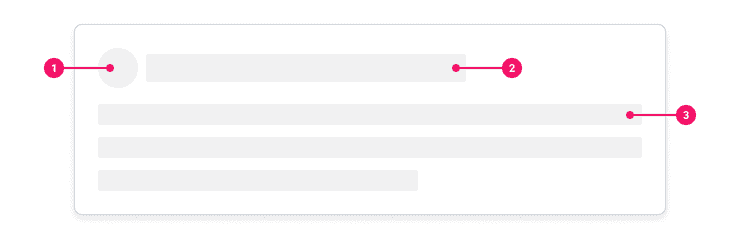
Anatomy
- Shape Skeleton: Represents graphical elements such as avatars, icons, and small Images.
- Header Skeleton: Represent headings and sub-headings.
- Text Skeleton: Represent paragraph and body text.
Usage Guidance
- A Skeleton should provide a close representation of the ultimate page layout and content once loaded.
- Use motion within the Skeleton to reinforce that the page is loading behind the scenes.
- Ideal for pages that require longer initial load times.
- Use for pages where all content loads at the same time.
- Meant to be used specifically on a white background.
When to Use
- Use Skeleton if the visual layout/format of the content being loaded is known ahead of time.
- Use specifically on pages where all or a majority of the page will be taking time to load.
When to Use Something Else
- If the visual layout/format of the content being loaded is unknown; or you need to indicate processing or that change will occur on the page (rather than loading UI elements), consider using a Loading Dots instead.
Examples
Basic Example
Skeleton includes a container Skeleton component and the following subcomponents:
Skeleton.Header, Skeleton.Text, and Skeleton.Shape. Each subcomponent can be used as a
placeholder for a particular type of content.
Here's an example of how you might compose Skeleton components (along with non-Skeleton components
such as Box and Flex) to create a loading placeholder for a piece of content comprised of an
icon, a heading, and some text.
And here's an example that simulates how that Skeleton might work in practice.
Press the Simulate Loading button to simulate the loading of the content (customize the loading time using the Load Time field), or check the Loading check box to force the Skeleton to display.
Color
All Skeleton subcomponents accept a backgroundColor prop which can be used to specify the color of
the subcomponent. This is generally only recommended to be used for dark or gray backgrounds to
ensure the Skeleton components are visible.
Text
Skeleton.Text renders a placeholder for text content such as paragraphs. Each placeholder line has
a width of 100% and a fixed height of 21px, with the last line having a width of 60% if there
are multiple lines.
Header
Skeleton.Header renders a placeholder for header content such as headings.
Shape
Skeleton.Shape renders a placeholder for graphic elements such as icons, avatars and small images.
Set the height, width, and borderRadius props of the Skeleton.Shape to create various
rectangular and circular shapes.
Component API
Skeleton
Skeleton subcomponents must be wrapped by the Skeleton container component.
<Skeleton><Skeleton.Header /><Skeleton.Text /></Skeleton>
Skeleton places its children in a container element with aria-hidden set to true and
announces itself using a visually hidden element.
Props
Props extend from div. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
aria-label | string | For accessibility reasons, IMPORTANT: Since we take over the use of | |
children | ReactNode | ||
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | div |
ref | React.Ref<R = div> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If |
Skeleton.Header
Skeleton.Header renders a placeholder for header content such as headings.
Props
Props extend from div. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
backgroundColor | string | The background color of the skeleton | |
height | number | string | The height of the shape in | '28px' |
width | number | string | The width of the shape in | '100%' |
children | React.ReactNode | ||
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | div |
ref | React.Ref<R = div> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If |
Skeleton.Text
Skeleton.Text renders a placeholder for text content such as paragraphs. Each placeholder
line has a width of 100% and a fixed height of 21px, with the last line having a width of
60% if there are multiple lines.
Props
Props extend from div. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
lineCount | number | The number of "lines" that SkeletonText will display. If there is more than one line, the last line will have a width of | 2 |
backgroundColor | string | The background color of the skeleton | |
children | React.ReactNode | ||
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | div |
ref | React.Ref<R = div> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If |
Skeleton.Shape
Skeleton.Shape renders a placeholder for graphic elements such as icons, avatars and small
images. Set the height, width, and borderRadius props of the Skeleton.Shape to create
various rectangular and circular shapes.
Props
Props extend from div. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
width | number | string | The width of the shape in | '100%' |
height | number | string | The height of the shape in | '100%' |
borderRadius | number | string | The borderRadius of the shape in | 0 |
backgroundColor | string | The background color of the skeleton | |
children | React.ReactNode | ||
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | div |
ref | React.Ref<R = div> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If |
Accessibility Guidelines
- A Skeleton should announce to users using a screen reader that content or a page is being loaded.
Content Guidelines
- Though the Skeleton component does not use actual content, the Header Skeleton and the Text Skeleton elements should be used as though they are actual content.
- The Header Skeleton will represent headings and sub-headings while the Text Skeleton will represent paragraph or body text.
Can't Find What You Need?
Check out our FAQ section which may help you find the information you're looking for.
FAQ Section