Menu
Menus display a list of up to 15 options when launched by an action or UI element like an icon or button.
Menu (Main) vs. Menu (Preview)
We recommend you use the Menu in the Main package (@workday/canvas-kit-react) documented here on
this page. The Menu in the Preview package (@workday/canvas-kit-preview-react) has been
marked for soft-deprecation in
Canvas Kit v8 and will be removed in v9.
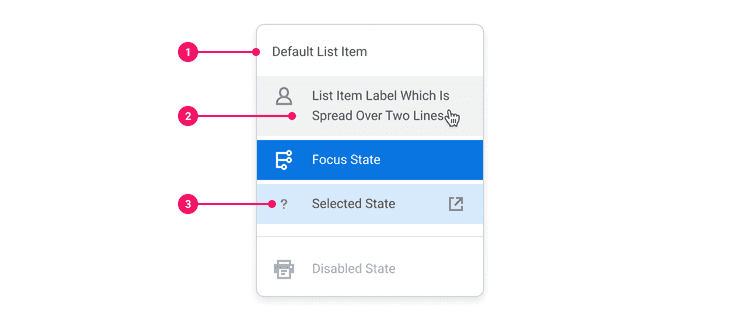
Anatomy
- Container: Rectangular container that houses the icon and text for menu list items.
- Text: Text for indicating where the link leads to when the menu is clicked on. Text can overflow to the next line but avoid going over more than two lines of text.
- Icons: Icons are optional and can be positioned before or after the text.
Usage Guidance
- Popup Menus can appear next to, in front of, above, or below the element that launched them, such as Dropdown Buttons, Dropdown Icons, icon only Primary/Secondary/Tertiary Button variants or by right-clicking a contextual item.
- Popup Menus should overlap and visually look like they are in front of other UI elements. They should always be positioned within the viewable areas of the screen and be 8px away from the element that launched them.
- Popup Menus should always contain a list of menu selections, which are options users can choose from. The list should be scannable, kept as concise as possible, and written in title case instead of sentences.
- Consider how important each option is. The list of options should be sorted in a logical order, such as alphabetical, chronological, order of importance, and so on.
When to Use
- In most cases, as with Overflow Menus, where there aren't enough space on screen to show all the actions, there could be between 1-7 items to choose from. However, there shouldn't be more than 15 items listed at once on a single Popup Menu.
- When users must make a single selection from the list of options.
When to Use Something Else
- Consider using a Switch if the only options are yes or no.
- For a list between 2 to 7 predefined options, consider using a Radio input to select one option or Checkboxes to select multiple options. Radio and Checkbox groups display all options upfront and do not require the user to interact with the input to view the list of options.
- Use a Prompt when the number of list items is large or unknown. Prompts have search capabilities and folders which provide users with the means to browse options. Prompts can be configured to support single or multi-select.
Examples
Basic Example
Menu is typically triggered by an action such as pressing a button. The Menu comes with a
Target subcomponent and a Popup.
Selected:
Menu will automatically focus on the cursor item (first item by default). The Menu uses a menu
model which composes a list model and a popup model and sets up accessibility features for you.
Menu follows the
Actions Menu pattern
using roving tabindex. Below is table of supported keyboard shortcuts and associated actions.
| Key | Action |
|---|---|
Enter or Space | Activates the menu item and then closes the menu |
Escape | Closes the menu |
Up Arrow | Moves focus to the previous menu item – if focus is on first menu item, it moves focus to the last menu item |
Down Arrow | Moves focus to the next menu item – if focus is on last menu item, it moves focus to the first menu item |
Home | Moves focus to the first menu item |
End | Moves focus to the last menu item |
Context Menu
Selected:
Icons
Menu supports more complex children, including icons, but the text of the item will no longer be
known. In this case, add a data-text attribute to inform the collection system what the text of
the item is. The text is used for components that filter based on text. For example, a Select
component will jump to an item based on the keys the user types. If the user types "C", the
component will jump to the first item that starts with a "C". This functionality requires knowledge
about the text of the item.
Selected:
Component API
Menu
Menu is a combination of a popup and a list. It usually has some type of target element that
expands/collapses the menu and a menu role and and several menuitem roles. Focus is managed
using roving tabindex for maximum
compatibility. A Menu can have two modes: single and multiple. This mode determines both
how many items can be selected as well as the default behavior when a menuitem is clicked. For
the single mode, selecting a menuitem will select and close the menu. For the multiple
mode, clicking a menuitem will toggle selection and will not close the menu.
<Menu><Menu.Target>Open</Menu.Target><Menu.Popper><Menu.Card><Menu.List><Menu.Item data-id="first">First Item</Menu.Item><Menu.Item data-id="second">Second Item</Menu.Item></Menu.List></Menu.Card></Menu.Popper></Menu>
Props
Props extend from . If a model is passed, props from MenuModelConfig are ignored.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
children | ReactNode | The contents of the Menu. Can be | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
Menu.Target
Menu.Target is similar to all types. The component only
provides behavior and no styling. The as prop is used to determine which component is
rendered. This component should forward the ref and apply any additional props directly to
an element. The default as is a . Any Canvas Kit component should
work with an as.
An example changing to a
<Menu.Target as={PrimaryButton}>Primary Button Text</Menu.Target>
This element will apply aria-haspopup and aria-expanded to inform screen readers there's
a popup associated with the element.
Props
Props extend from . Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
children | ReactNode | ||
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | |
ref | React.Ref<R = > | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
Menu.Card
The menu card is a non-semantic element used to give the dropdown menu its distinct visual cue that the dropdown menu is floating above other content. A menu card usually contains a menu list, but can also contain other elements like a header or footer.
Layout Component
Menu.Card supports all props from thelayout component.
Props
Props extend from div. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
children | ReactNode | Children of the Card. Should contain a | |
cs | | The
| |
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | div |
ref | React.Ref<R = div> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
Menu.List
The menu list follows the Collections API. A list can either contain static items
or a render prop and items to the model.
const MyComponent = () => {const model = useMenuModel({items: [{ id: 'first', text: 'First Item' },{ id: 'second', text: 'Second Item' },]})return (<Menu model={model}><Menu.List>{(item) => <Menu.Item data-id={item.id}>{item.text}</Menu.Item>}</Menu.List></Menu>)}
Layout Component
Menu.List supports all props from thelayout component.
Props
Props extend from div. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
children | ReactNode | ((item: T) => ReactNode) | The label text of the MenuList. | |
cs | | The
| |
columnCount | number | If this is set it will cause a wrapping of a list that will turn it into a grid | 0 |
id | string | IDREF of the list. Children ids can be derived from this id | |
select | (data: { | Select a specific item by its identifier. | |
orientation | | The orientation of a list of items. Values are either | 'vertical' |
navigation | | Controls the state changes when the user sends navigation events to the model. For example,
when the user hits the "right" arrow, a behavior hook will determine directionality
(left-to-right or right-to-left) and call the correct navigation method. In our example, a
left-to-right language would send a An example override might be a tab list with an overflow menu that is meant to be transparent to screen reader users. This would require the overflow menu to accept both up/down keys as well as left/right keys to give a more consistent experience to all users. | |
getId | (item: ) => string | Optional function to return an id of an item. If not provided, the default function will
return the | |
getTextValue | (item: ) => string | Optional function to return the text representation of an item. If not provided, the default
function will return the | |
nonInteractiveIds | string[] | Array of all ids which are currently disabled. This is used for navigation to skip over items which are not focusable. | |
defaultItemHeight | number | Best guess to the default item height for virtualization. Getting this number correct avoids a rerender while the list is initializing. | 50 |
shouldVirtualize | true | ||
items | [] | Optional array of items. If provided, use a render prop for list children instead of static
children. If the shape of each item object does not have an | |
registerItem | (data: { | Register an item to the list. Takes in an identifier, a React.Ref and an optional index. This should be called on component mount. This event is only called for static rendering. | |
unregisterItem | (data: { | Unregister an item by its identifier. This should be called when the component is unmounted. This event is only called for static rendering. | |
updateItemHeight | (data: { | Updates the default item height. This should only be called when item height is measured. Calling this with a different default item height than previous will cause a virtual list to recalculate the overall height of the list and invalidate any height caching. Doing this only on the first item may save the user from experiencing odd scrolling behavior where the scrollbar updates while scrolling. If the user uses the mouse to drag the bar, it can become "detached" since the browser recalculates scroll bar position while the overflow container is updated. | |
registerItem | (data: { | Register an item to the list. Takes in an identifier, a React.Ref and an optional index. This should be called on component mount. This event is only called for static rendering. | |
unregisterItem | (data: { | Unregister an item by its identifier. This should be called when the component is unmounted. This event is only called for static rendering. | |
updateItemHeight | (data: { | Updates the default item height. This should only be called when item height is measured. Calling this with a different default item height than previous will cause a virtual list to recalculate the overall height of the list and invalidate any height caching. Doing this only on the first item may save the user from experiencing odd scrolling behavior where the scrollbar updates while scrolling. If the user uses the mouse to drag the bar, it can become "detached" since the browser recalculates scroll bar position while the overflow container is updated. | |
initialCursorId | string | Initial cursor position. If not provided, the cursor will point to the first item in the list | |
pageSize | number | Controls how much a pageUp/pageDown navigation request will jump. If not provided, the size of the list and number of items rendered will determine this value. | |
goTo | (data: { | Directly sets the cursor to the list item by its identifier. | |
goToNext | () => void | Set the cursor to the "next" item in the list. This event delegates to the | |
goToPrevious | () => void | Set the cursor to the "previous" item in the list. If the beginning of the list is detected, it will wrap to the last item | |
goToPreviousRow | () => void | Previous item perpendicular to the orientation of a list, or the previous row in a grid. For
example, if a list is horizontal, the previous row would describe an up direction. This could
be ignored by the navigation manager, or return the same result as | |
goToNextRow | () => void | Next item perpendicular to the orientation of a list, or the next row in a grid. For example,
if a list is horizontal, the next row would describe a down direction. This could be ignored by
the navigation manager, or return the same result as | |
goToFirst | () => void | Set the cursor to the first item in the list | |
goToLast | () => void | Set the cursor to the last item in the list | |
goToFirstOfRow | () => void | ||
goToLastOfRow | () => void | ||
goToNextPage | () => void | ||
goToPreviousPage | () => void | ||
goTo | (data: { | Directly sets the cursor to the list item by its identifier. | |
goToNext | () => void | Set the cursor to the "next" item in the list. This event delegates to the | |
goToPrevious | () => void | Set the cursor to the "previous" item in the list. If the beginning of the list is detected, it will wrap to the last item | |
goToPreviousRow | () => void | Previous item perpendicular to the orientation of a list, or the previous row in a grid. For
example, if a list is horizontal, the previous row would describe an up direction. This could
be ignored by the navigation manager, or return the same result as | |
goToNextRow | () => void | Next item perpendicular to the orientation of a list, or the next row in a grid. For example,
if a list is horizontal, the next row would describe a down direction. This could be ignored by
the navigation manager, or return the same result as | |
goToFirst | () => void | Set the cursor to the first item in the list | |
goToLast | () => void | Set the cursor to the last item in the list | |
goToFirstOfRow | () => void | ||
goToLastOfRow | () => void | ||
goToNextPage | () => void | ||
goToPreviousPage | () => void | ||
initialSelectedIds | | ||
initialUnselectedIds | string[] | ||
selection | | ||
selectAll | () => void | Select all items. This will set | |
unselectAll | () => void | Unselect all items. | |
select | (data: { | Select a specific item by its identifier. | |
selectAll | () => void | Select all items. This will set | |
unselectAll | () => void | Unselect all items. | |
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | div |
ref | React.Ref<R = div> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
useMenuList
(
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {
role: string;
aria-labelledby: string;
},
,
)Menu.Item
A Menu.Item has an optional data-id prop that identifies the item in the Menu.List and
will be passed to the optional onSelect callback of the Menu model. A Menu.Item can
contain any HTML. If more complex HTML is provided, add data-text to the Menu.Item
component if using the static API. If you're using the dynamic API, pass getTextValue to
the model.
Props
Props extend from button. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
index | number | Optionally pass index to menu item. This should be done if | |
children | ReactNode | The label text of the MenuItem. | |
data-id | string | The name of the menu item. This name will be used in the | |
aria-disabled | boolean | ||
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | button |
ref | React.Ref<R = button> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
useMenuItem
(
(
model: ,
elemProps: {
data-id: string;
},
ref: React.Ref
) => {
ref: (instance: | null) => void;
role: string;
onClick: ((event: SyntheticEvent) => void) | undefined;
},
,
,
)Menu.Divider
Props
Props extend from hr. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
children | React.ReactNode | ||
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | hr |
ref | React.Ref<R = hr> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If |
Menu.TargetContext
A Menu.TargetContext is the same as a , except it adds a
context event handler instead of a click handler to trigger context menus.
Props
Props extend from . Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
children | ReactNode | ||
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | |
ref | React.Ref<R = > | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
Menu.Popper
The "Popper" of a menu. The popper will appear around the . It
renders a div element that is portalled to the document.body which is controlled by the
. The PopupStack is not part of React. This means no extra props given to
this component will be forwarded to the div element, but the ref will be forwarded.
Props
Props extend from div. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
anchorElement | <Element> | Element | null | The reference element used to position the Popper. Popper content will try to follow the
| |
children | ((props: { | The content of the Popper. If a function is provided, it will be treated as a Render Prop and
pass the | |
getAnchorClientRect | () => | When provided, this optional callback will be used to determine positioning for the Popper element
instead of calling | |
open | boolean | Determines if | true |
placement | | The placement of the | |
fallbackPlacements | [] | Define fallback placements by providing a list of | |
onPlacementChange | (placement: ) => void | A callback function that will be called whenever PopperJS chooses a placement that is different
from the provided | |
popperOptions | <PopperOptions> | The additional options passed to the Popper's | |
portal | boolean | If false, render the Popper within the
DOM hierarchy of its parent. A non-portal Popper will constrained by the parent container
overflows. If you set this to | true |
popperInstanceRef | Ref<> | Reference to the PopperJS instance. Useful for making direct method calls on the popper
instance like | |
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | div |
ref | React.Ref<R = div> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
usePopupPopper
Adds the necessary props to a component. Used by the
subcomponent.
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {
open: boolean;
anchorElement: <>;
ref: (instance: | null) => void;
onPlacementChange: (placement: ) => void;
}Model
Specifications
| Given | When | Then |
|---|---|---|
| the Basic story is rendered |
| |
| the Basic story is rendered |
| |
| the Basic story is rendered |
| |
| the Basic story is rendered |
| |
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic story is rendered |
|
|
| the MenuWithFallbackPlacements example is rendered |
|
|
| the MenuWithFallbackPlacements example is rendered |
|
|
| the MenuWithFallbackPlacements example is rendered |
|
|
Accessibility Guidelines
Keyboard Interaction
Each menu item must have a focus indicator that is highly visible against the background and against the non-focused state. Refer to Accessible Colors for more information.
Menus must support the following keyboard interactions:
EnterorSpace: activates the focused menu itemEsc: dismisses the opened menu and returns focus to the button that invoked the menuUp ArroworDown Arrow: navigates among the menu items cyclicallyHomeorEnd: navigates to the first menu item, or the last menu item respectively
Screen Reader Interaction
Menus must communicate the following to users:
- A button will invoke a menu or popup
- Focus has been moved into an opened menu
- The correct number of items in the menu
- The name of the focused menu item
Design Annotations Needed
- Write an accessible name for icon-only button variants invoking menus.
- Declare whether any icons used in menu items are decorative, or require additional text alternatives.
Implementation Markup Needed
- For buttons invoking menus, an
aria-haspopup=”true”property and anaria-expandedattribute must be added. - [Included in component] The menu container must have an ARIA `role=”menu” attribute.
- [Included in component] All child elements inside the menu container must have an ARIA `role=”menuitem” attribute.
- [Included in component] Use
“roving tabindex” technique
for managing focus inside the menu. Set
tabindex=”0”on the focused menu item, and set to”-1”on remaining menu items.
Content Guidelines
- When writing Menu list items, refer to the Menus section of the Content Style Guide.
Can't Find What You Need?
Check out our FAQ section which may help you find the information you're looking for.
FAQ Section