Popup
Custom popups communicate relevant and timely information to users in response to user action or through system-generated messages.
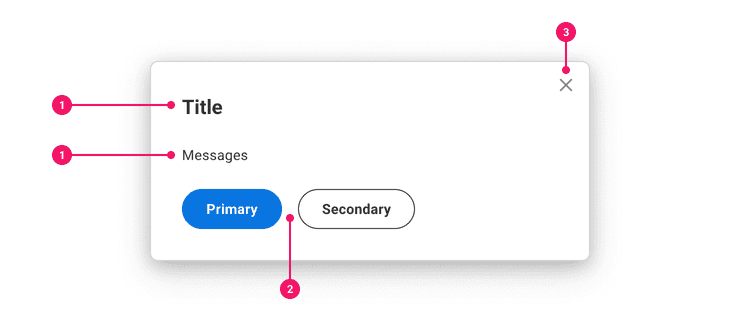
Anatomy
- Title (Optional): Titles should display the title of the content or dialog.
- Content: Popups contain different types of content. Typical types of content include alerts and dialogs.
- Buttons(Optional): When there is a user action, use the action bar. When displaying informational content, use in-line buttons.
- Close “X” Icon (Optional): Users are able to intentionally dismiss a popup.
Usage Guidance
Popup components are generally used in place of Non-Modal Dialogs. Because Non-Modal Dialogs only minimally obstruct the page, they are ideal for drawing attention to optional, non-critical information or new features while keeping page content still visible. Popups appear within the context of a page and do not interrupt normal workflow.
When to use
- Use Popups when needing to customize a popup element beyond the offerings of other popup components such as a Modal, Tooltip, etc.
- Do make Popups easily dismissible in context of the trigger element.
- The popup component is used to display content that doesn’t fit the use cases of more specific notification components such as Tooltips, Modals, Dropdown menus, etc.
- Popups can be used to display confirmation messages, validate user inputs, or display short informational content in the context of a user action.
When to Use Something Else
- Do not use Popups to display dense information, such as Tables or Multi-View Containers.
- Popups are easy to dismiss. Consider using a Modal if you require more user attention or interactive form components in your popup.
- Consider a Toast if you are communicating status or confirmation of the application process to the user.
- Consider a Menu if the input is a single selection of options.
- Use a Tooltip to add context a button, link, to other element.
- See Notifications and Errors and Alerts guidance in the Patterns section for more information on types of notifications and their use cases.
Examples
The Popup component is a generic
Compound Component that is used to
build popup UIs that are not already covered by Canvas Kit.
Basic Example
The Popup has no pre-defined behaviors built in, therefore the usePopupModel must always be used
to create a new model. This model is then used by all behavior hooks to apply additional popup
behaviors to the compound component group. The following example creates a typical popup around a
target element and adds useCloseOnOutsideClick, useCloseOnEscape, useInitialFocus, and
useReturnFocus behaviors. You can read through the hooks section to learn about all the
popup behaviors. For accessibility, these behaviors should be included most of the time.
Initial Focus
If you want focus to move to a specific element when the popup is opened, set the initialFocusRef
of the model. Check with accessibility before doing this. The following example sets the focus on
the "OK" button with an aria-describedby pointing to the model's id state so screen readers
properly announce the message of the popup when focus is changed to the button. By default, focus
will be placed on the first focusable element when the popup is opened.
Focus Redirect
Focus management is important to accessibility of popup contents. The following example shows
useFocusRedirect being used to manage focus in and out of a Popup. This is very useful for
Dialog-style popups. Since Popup.Popper renders contents to the bottom of the document body,
aria-owns is used for screen readers that support it. This effectively treats a Popup like it
exists in between the buttons while it is opened. Screen readers will navigate the content as if the
content was not portalled to the bottom of the document body. Focus redirection tries to treat the
Popup as if it were inline to the document. Tabbing out of the Popup will close the Popup and move
focus to the next appropriate element.
Note: Safari does not support
aria-owns. This means that the contents of the Popup will appears out of order to Safari + VoiceOver users. We render popups at the bottom of the document.body to ensure proper rendering. You could useportal=falseon thePoppercomponent, but that would risk incorrect rendering in all browsers.
Focus Trapping
Focus trapping is similar to the Focus Redirect example, but will trap focus inside the popup instead of redirecting focus, it will be trapped inside the Popup. This is most useful for modal dialogs where the modal must be interacted with before normal interaction can continue.
Note: Using focus trapping outside a Modal context can give users a different experience depending on how they interact with your application. Focus trapping will not prevent mouse users from breaking out of a focus trap, nor will it prevent screen reader users from using virtual cursors from breaking out. Modals should use additional techniques to truely "trap" focus into the Popup to provide a consistent experience for all users.
Multiple Popups
If you need multiple Popups within the same component, you can create multiple models and pass a unique model to each Popup. Below is an example of 2 different popups within the same component. Since each Popup gets its own model, each Popup behaves independently. The same technique can be used for nested Popups.
Nested Popups
If you need nested Popups within the same component, you can create multiple models and pass a
unique model to each Popup. Popup comes with a Popup.CloseButton that uses a Button and adds
props via the usePopupCloseButton hook to ensure the popups hides and focus is returned. The as
can be used in a powerful way to do this by using <Popup.CloseButton as={Popup.CloseButton}> which
will mix in click handlers from both popups. This is not very intuitive, however. You can create
props that merge a click handler for both Popups by using usePopupCloseButton directly. The second
parameter is props to be merged which will effectively hide both popups. Focus management is
preserved.
Custom Target
It is common to have a custom target for your popup. Use the as prop to use your custom component.
The Popup.Target element will add onClick and ref to the provided component. Your provided
target component must forward the onClick to an element for the Popup to open. The as will cause
Popup.Target to inherit the interface of your custom target component. This means any props your
target requires, Popup.Target now also requires. The example below has a MyTarget component that
requires a label prop.
Note: If your application needs to programmatically open a Popup without the user interacting with the target button first, you'll also need to use
React.forwardRefin your target component. Without this, the Popup will open at the top-left of the window instead of around the target.
Full Screen API
By default, popups are created as children of the document.body element, but the PopupStack
supports the Fullscreen API. When
fullscreen is entered, the PopupStack will automatically create a new stacking context for all
future popups. Any existing popups will disappear, but not be removed. They disappear because the
fullscreen API is only showing content within the fullscreen element. There are instances where a
popup may not close when fullscreen is exited:
- The escape key is used to exit fullscreen
- There is a button to exit fullscreen, but the popup doesn't use
useCloseOnOutsideClick
If fullscreen is exited, popups within the fullscreen stacking context are not removed or transferred automatically. If you do not handle this case, the popup may not render correctly. This example shows a popup that closes when fullscreen is entered/exited and another popup that transfers the popup's stack context when entering/exiting fullscreen.
RTL
The Popup component automatically handles right-to-left rendering.
Note: This example shows an inaccessible open card for demonstration purposes.
למחוק פריט
האם ברצונך למחוק פריט זה
Component API
Popper
A thin wrapper component around the Popper.js positioning engine. For reference:
https://popper.js.org/. Popper also automatically works with the system.
Popper has no UI and will render any children to the body element and position around a
provided anchorElement.
Prefer using instead. Use this to make Popups that don't utilize
a PopupModel or any associate popup hooks.
Note:
Popperrenders any children to adivelement created by thePopupStack. This element is not controlled by React, so any extra element props will not be forwarded. Therefwill point to thedivelement created by thePopupStack, however. In v4, an extradivelement was rendered and that's where extra props were spread to. In v5+, you can provide your own element if you wish.
Props
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
anchorElement | <Element> | Element | null | The reference element used to position the Popper. Popper content will try to follow the
| |
children | ((props: { | The content of the Popper. If a function is provided, it will be treated as a Render Prop and
pass the | |
getAnchorClientRect | () => | When provided, this optional callback will be used to determine positioning for the Popper element
instead of calling | |
open | boolean | Determines if | true |
placement | | The placement of the | |
fallbackPlacements | [] | Define fallback placements by providing a list of | |
onPlacementChange | (placement: ) => void | A callback function that will be called whenever PopperJS chooses a placement that is different
from the provided | |
popperOptions | <PopperOptions> | The additional options passed to the Popper's | |
portal | boolean | If false, render the Popper within the
DOM hierarchy of its parent. A non-portal Popper will constrained by the parent container
overflows. If you set this to | true |
popperInstanceRef | Ref<> | Reference to the PopperJS instance. Useful for making direct method calls on the popper
instance like |
Popup
This component is a container component that has no semantic element. It provides a React Context
model for all Popup subcomponents. A model can be manually passed to subcomponents to override
the model context.
// using Popup<Popup model={model}><Popup.Target /> // no model here</Popup>// using models on subcomponents<><Popup.Target model={model} /></>
Props
Props extend from . If a model is passed, props from PopupModelConfig are ignored.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
children | ReactNode | The contents of the Popup. Can be | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
Popup.Target
A Popup.Target is any element that is meant to show the Popup. The default component
rendered by this component is a element. You can override this by
passing the desired component via as. Many examples above use as={DeleteButton}. If you
want to render a instead, use as={TertiaryButton}. The behavior hook
used is called .
const model = usePopupModel();// using this component<Popup.Target>Show Popup</Popup.Target>// using props insteadconst popupTargetButtonProps = usePopupTarget(model);<SecondaryButton {...popupTargetButtonProps}>Show Popup</SecondaryButton>
Popup.Target doesn't provide any styling by default. All styling comes from the default
component used, which is . If you don't want any styling, you can do
the following:
<Popup.Target as="button">Open</Popup.Target>
To add your own styling, you could either add a css prop, or make a styled button and pass
that styled component via the as prop.
Props
Props extend from . Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
usePopupTarget
Adds the necessary props to a subcomponent.
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {
ref: (instance: | null) => void;
onClick: (event: ) => void;
}Popup.Popper
A Popup.Popper is a component that is hooked up to the automatically. The behavior hook used is called .
Note:
Popup.Popperrenders any children to adivelement created by the. This element is not controlled by React, so any extra element props will not be forwarded. Therefwill point to thedivelement created by thePopupStack, however. If you wish to add extra props to an element, add them to theinstead.
Props
Props extend from div. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
placement | | The placement of the | |
fallbackPlacements | [] | Define fallback placements by providing a list of | |
popperOptions | <PopperOptions> | The additional options passed to the Popper's | |
anchorElement | <Element> | Element | null | The reference element used to position the Popper. Popper content will try to follow the
| |
children | ((props: { | The content of the Popper. If a function is provided, it will be treated as a Render Prop and
pass the | |
getAnchorClientRect | () => | When provided, this optional callback will be used to determine positioning for the Popper element
instead of calling | |
open | boolean | Determines if | true |
onPlacementChange | (placement: ) => void | A callback function that will be called whenever PopperJS chooses a placement that is different
from the provided | |
portal | boolean | If false, render the Popper within the
DOM hierarchy of its parent. A non-portal Popper will constrained by the parent container
overflows. If you set this to | true |
popperInstanceRef | Ref<> | Reference to the PopperJS instance. Useful for making direct method calls on the popper
instance like | |
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | div |
ref | React.Ref<R = div> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
usePopupPopper
Adds the necessary props to a component. Used by the
subcomponent.
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {
open: boolean;
anchorElement: <>;
ref: (instance: | null) => void;
onPlacementChange: (placement: ) => void;
}Popup.Card
A Popup.Card is a wrapper around the component, but hooked up to a
. By default, this element has a role=dialog and an aria-labelledby.
The behavior hook used is called .
Layout Component
Popup.Card supports all props from thelayout component.
Props
Props extend from div. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
children | ReactNode | Children of the Card. Should contain a | |
cs | | The
| |
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | div |
ref | React.Ref<R = div> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
usePopupCard
Adds the necessary props to a subcomponent.
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {
role: string;
aria-labelledby: string;
}Popup.CloseIcon
A Popup.CloseIcon is an icon button that is the X in the top of a popup. It will hide a
popup when clicked. The behavior hook used is called .
Layout Component
Popup.CloseIcon supports all props from thelayout component.
Props
Props extend from button. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
variant | 'inverse' | Variant has an option for | |
isThemeable | boolean | ||
iconPosition | 'start' | 'end' | Button icon positions can either be | 'start' |
fill | string | The fill color of the SystemIcon. This overrides | |
background | string | The background color of the SystemIcon. | |
color | string | The color of the SystemIcon. This defines | |
shouldMirror | boolean | If set to | false |
cs | | The
| |
children | ReactNode | ||
icon | | The icon of the Button.
Note: Not displayed at | |
size | | There are four button sizes: | |
accent | string | The accent color of the SystemIcon. This overrides | |
accentHover | string | The accent color of the SystemIcon on hover. This overrides | |
backgroundHover | string | The background color of the SystemIcon on hover. | |
colorHover | string | The hover color of the SystemIcon. This defines | |
fillHover | string | The fill color of the SystemIcon on hover. This overrides | |
colors | | Override default colors of a button. The default will depend on the button type | |
fillIcon | boolean | Whether the icon should received filled (colored background layer) or regular styles.
Corresponds to | |
shouldMirrorIcon | boolean | If set to | false |
grow | boolean | True if the component should grow to its container's width. False otherwise. | |
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | button |
ref | React.Ref<R = button> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
usePopupCloseButton
Adds the necessary props to a close button component. Used by the
subcomponent and
subcomponent.
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {
onClick: (event: Event | SyntheticEvent) => void;
}Popup.Heading
A Popup.Heading is a wrapper around that connect the
heading to a . It will add an id to the element that match the
aria-labelledby that is applied to the Popup.Card element for accessibility. The behavior
hook used is called .
Layout Component
Popup.Heading supports all props from thelayout component.
Props
Props extend from h2. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
children | ReactNode | ||
id | string | The id of the Card heading. Tie this to an | |
cs | | The
| |
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | h2 |
ref | React.Ref<R = h2> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
usePopupHeading
Adds the necessary props to the subcomponent.
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {
id: string;
}Popup.Body
A Popup.Body is a thin wrapper around and doesn't actually take
a model. It adds body styling and nothing else.
Layout Component
Popup.Body supports all props from thelayout component.
Props
Props extend from div. Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
cs | | The
| |
children | ReactNode | ||
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | div |
ref | React.Ref<R = div> | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
Popup.CloseButton
A Popup.CloseButton is a button that will hide a popup. By default, this is a
component, but as can be used to render any button element (i.e
or ). The behavior hook used is called
.
Props
Props extend from . Changing the as prop will change the element interface.
| Name | Type | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
children | ReactNode | ||
as | React.ElementType | Optional override of the default element used by the component. Any valid tag or Component. If you provided a Component, this component should forward the ref using Note: Not all elements make sense and some elements may cause accessibility issues. Change this value with care. | |
ref | React.Ref<R = > | Optional ref. If the component represents an element, this ref will be a reference to the real DOM element of the component. If | |
model | | Optional model to pass to the component. This will override the default model created for the component. This can be useful if you want to access to the state and events of the model, or if you have nested components of the same type and you need to override the model provided by React Context. | |
elemPropsHook | ( | Optional hook that receives the model and all props to be applied to the element. If you use this, it is your responsibility to return props, merging as appropriate. For example, returning an empty object will disable all elemProps hooks associated with this component. This allows finer control over a component without creating a new one. |
usePopupCloseButton
Adds the necessary props to a close button component. Used by the
subcomponent and
subcomponent.
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {
onClick: (event: Event | SyntheticEvent) => void;
}Model
Hooks
usePopupStack
Note: If you're using , you do not need to use this hook directly.
This hook will add the stackRef element to the on mount and remove on unmount. If
you use Popper, the popper stackRef is automatically added/removed from the PopupStack. The
PopupStack is required for proper z-index values to ensure Popups are rendered correct. It is
also required for global listeners like click outside or escape key closing a popup. Without the
PopupStack, all popups will close rather than only the topmost one.
If ref is provided, it will be the same as stackRef. If ref is not provided`,
this hook will create one and return it.
This hook should be used by all stacked UIs unless using the Popper component.
const model = usePopupModel();usePopupStack(model.state.stackRef, model.state.targetRef);// add some popup functionalityuseCloseOnOutsideClick(model);useCloseOnEscape(model);return (<><button ref={model.state.targetRef}>Open Popup</button>{model.state.visibility !== 'hidden'? ReactDOM.createPortal(<div>Popup Contents</div>, model.state.stackRef.current): null}</>);
<E extends >(
ref: Ref<E>,
target: | <>
) => <>useAssistiveHideSiblings
This hook will hide all sibling elements from assistive technology. Very useful for modal
dialogs. This will set aria-hidden for sibling elements of the provided PopupModel's
state.stackRef element and restore the previous aria-hidden to each component when the
component is unmounted. For example, if added to a Modal component, all children of
document.body will have an aria-hidden=true applied except for the provided stackRef
element (the Modal). This will effectively hide all content outside the Modal from assistive
technology including Web Rotor for VoiceOver for example.
This should be used on popup elements that need to hide content (i.e. Modals).
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {}useBringToTopOnClick
This hook will bring an element to the top of the stack when any element inside the provided
's state.stackRef element is clicked. If was
used or PopupStack.add provided an owner, all "child" popups will also be brought to the top.
A "child" popup is a Popup that was opened from another Popup. Usually this is a Tooltip or
Select component inside something like a Modal.
This should be used on popup elements that are meant to persist (i.e. Windows).
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {}useCloseOnEscape
Registers global detection of the Escape key. It will only call the 's hide
event if the provided model's state.stackRef element is the topmost in the stack.
This should be used with popup elements that are dismissible like Tooltips, Modals, non-modal dialogs, dropdown menus, etc.
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {}useCloseOnOutsideClick
Registers global listener for all clicks. It will only call the 's hide event
if the click happened outside the PopupModel's state.stackRef element and its children and
the provided stackRef element is the topmost element with this behavior applied in the stack.
Adds a data-behavior-click-outside-close="topmost" attribute to ensure proper functionality.
This should be used with popup elements that are dismissible like Modals, non-modal dialogs,
dropdown menus, etc. Tooltips and hierarchical menus should use
instead.
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {}useAlwaysCloseOnOutsideClick
Registers global listener for all clicks. It will only call the PopupModel's hide event if the
click happened outside the stackRef element and its children regardless of the position in the
stack. This is useful for Tooltips or hierarchical menus. Adds a
data-behavior-click-outside-close="always" attribute to ensure proper functionality.
This should be used with popup elements that should close no matter their position in the stack (i.e. Tooltips).
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {}useAlwaysCloseOnOutsideClick
Registers global listener for all clicks. It will only call the PopupModel's hide event if the
click happened outside the stackRef element and its children regardless of the position in the
stack. This is useful for Tooltips or hierarchical menus. Adds a
data-behavior-click-outside-close="always" attribute to ensure proper functionality.
This should be used with popup elements that should close no matter their position in the stack (i.e. Tooltips).
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {}useCloseOnTargetHidden
Sets up an IntersectionObserver for the target element. When the target is detected as being less than 50% visible, the popup will close. Most likely, this will happen if the user scrolls an overflowed content area of the page and the target is no longer visible.
This should be used with popup elements that are transitory like Tooltips and dropdown menus.
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {}useDisableBodyScroll
Disables body scroll by adding overflow: hidden to the body element. This effectively prevents
page scrolling while the popup is visible.
This should be used with popup elements that hide all other content and force the user to accept or dismiss the popup before continuing (i.e. Modals).
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {}useFocusRedirect
Manages focus around a popup, treating the popup as if it was part of the DOM where it appears.
Popups are typically "portalled" (inserted at the end of document.body) to ensure proper
rendering. This violates WCAG Focus
Order. This
hook helps redirect focus as if the popup element appeared in the DOM. aria-owns might also be
used to ensure assistive technology places the popup after the button for virtual cursors. This
hook does no provide aria-owns and this must be provided yourself. Requires useReturnFocus to
work properly. Works well with useInitialFocus.
This should be used with non-modal dialogs.
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {}useFocusTrap
"Trap" or "loop" focus within a provided stackRef element. This is required for accessibility
on modals. If a keyboard users hits the Tab or Shift + Tab, this will force "looping" of focus.
It effectively "hides" outside content from keyboard users. Use an overlay to hide content from
mouse users and useAssistiveHideSiblings to hide content from assistive technology users. Works
well with useInitialFocus and useReturnFocus.
This should be used on popup elements that need to hide content (i.e. Modals).
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {}useInitialFocus
Moves focus within the popup when the popup becomes visible. This is useful for keyboard and
screen reader users alike. This should be used with or
for a complete focus management solution.
This should be used for popups that have focusable elements inside, like Modals, non-modal dialogs, menus, etc.
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {}useReturnFocus
Returns focus to the target element when the popup is hidden. This works well with
. This should be used with or
for a complete focus management solution.
This should be used on popup elements that use useInitialFocus.
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {}useTransferOnFullscreenEnter
Makes the popup transfer to the fullscreen element when fullscreen is entered. Without this, the popup would seem to disappear because the popup container element is not a child of the fullscreen element.
Don't use this in conjunction with a hook that will close the popup when entering fullscreen. Doing so would open the popup when the intention was to close it.
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {}useTransferOnFullscreenExit
Makes the popup transfer to fullscreen when fullscreen is exited. Without this hook, the popup would not operate correctly with other popups on the screen.
Don't use this in conjunction with a hook that will close the popup when exiting fullscreen. Doing so would open the popup when the intention was to close it.
(
model: ,
elemProps: {},
ref: React.Ref
) => {}Specifications
| Given | When | Then |
|---|---|---|
| the Basic example is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic example is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic example is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic example is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic example is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic example is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic example is rendered |
|
|
| the Basic example is rendered |
|
|
| the MultiplePopups example is rendered |
|
|
| the MultiplePopups example is rendered |
|
|
| the MultiplePopups example is rendered |
|
|
| the PopupWithNonHidablePopup example is rendered |
|
|
| the PopupWithNonHidablePopup example is rendered |
|
|
| the PopupWithNonHidablePopup example is rendered |
|
|
| the PopupWithNonHidablePopup example is rendered |
|
|
| the MixedPopupTypes story is rendered |
| |
| the MixedPopupTypes story is rendered |
|
|
| the MixedPopupTypes story is rendered |
|
|
| the MixedPopupTypes story is rendered |
|
|
| the MixedPopupTypes story is rendered |
|
|
| the MixedPopupTypes story is rendered |
|
|
| the MixedPopupTypes story is rendered |
|
|
| the MixedPopupTypes story is rendered |
|
|
| the MixedPopupTypes story is rendered |
|
|
| the MixedPopupTypes story is rendered |
|
|
| the MixedPopupTypes story is rendered |
|
|
| the MixedPopupTypes story is rendered |
|
|
| the MixedPopupTypes story is rendered |
|
|
| the MixedPopupTypes story is rendered |
|
|
| the MixedPopupTypes story is rendered |
|
|
| the MixedPopupTypes story is rendered |
|
|
| the MixedPopupTypes story is rendered |
|
|
| the MixedPopupTypes story is rendered |
|
|
| the CustomTarget example is rendered |
|
|
| the CustomTarget example is rendered |
|
|
| the CustomTarget example is rendered |
|
|
| the FocusRedirect example is rendered |
|
|
| the FocusRedirect example is rendered |
|
|
| the FocusRedirect example is rendered |
|
|
| the TooltipReturnFocus example is rendered |
|
|
| the TooltipReturnFocus example is rendered |
|
|
| the TooltipReturnFocus example is rendered |
|
|
| the ComboboxWithinPopup example is rendered |
|
|
| the ComboboxWithinPopup example is rendered |
|
|
| the PopupWithFallbackPlacements example is rendered |
|
|
| the PopupWithFallbackPlacements example is rendered |
|
|
| the PopupWithFallbackPlacements example is rendered |
|
|
Content Guidelines
- See the Dialogs, Popups, and Modals page in the UI Text section of the Content Style Guide for modal language guidelines.
Can't Find What You Need?
Check out our FAQ section which may help you find the information you're looking for.
FAQ Section